细胞外基质是由细胞产生和分泌,以提供结构和功能支持的结缔组织成分,执行和促进不同的细胞功能,对细胞的黏附、迁移、增殖和分化能够产生重要影响
[8-11] 。细胞外基质是由蛋白质和黏多糖等成分聚合而成的复杂网状支架,其成分主要包括糖胺多糖、蛋白聚糖、胶原和非胶原糖蛋白,在细胞外基质中胶原蛋白是最丰富的糖蛋白
[12] 。细胞外基质以间质基质和基底膜的形式存在于组织中,间质基质填充在细胞间隙内,支持并连接组织结构,缓冲和阻挡来自外部的压力,以保护细胞免受应力损伤。与此不同的是,基底膜是锚定各种上皮细胞和内皮细胞的细胞外基质层。 在细胞培养中,细胞外基质是指由细胞分泌的细胞生长环境,调节细胞的生理活动。
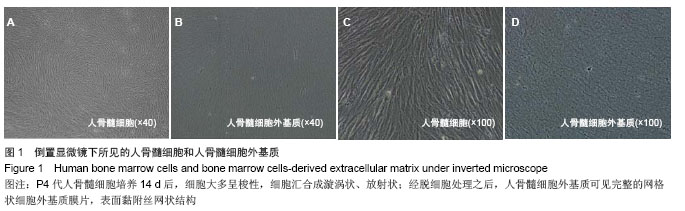
细胞外基质是组织或器官等天然物质经脱细胞处理之后所得的生物材料支架。脱细胞的目的是能够彻底去除细胞和胞核碎片,避免引起宿主免疫反应,最大限度地降低对组织重建的不利影响,同时又需要保持完整的网状结构,将生物活性的损失减少到最小。Grillo 等在1964年首次对皮肤进行脱细胞处理获得皮肤细胞外基质支架,自此之后出现多种去细胞的方法,常用的方法主要有:①物理法,如反复冻融法、压力法等。②化学试剂,如SDS、 CHAPS、TritonX-100等。③生物酶消化法,如胰蛋白酶、中性蛋白酶和核酸酶等
[13] 。物理方法主要是破坏细胞膜使细胞裂解,但是物理法不能将细胞脱离细胞外基质,必须结合化学试剂将细胞碎片清洗干净。化学试剂主要是破坏核酸、蛋白和脂质之间的连接,溶解破坏生物膜。生物酶主要增进细胞碎片与细胞外基质的分离。目前多采用联合去污剂和生物酶协同作用,更加彻底地去除残留的细胞碎片。
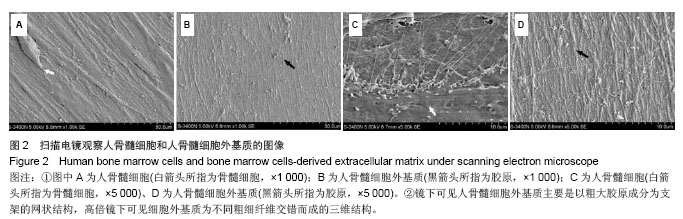
但是任何脱细胞的处理方法都会对细胞外基质的三维结构造成不同程度的影响,因此需要针对不同组织来源、细胞种类选择最佳的脱细胞的方法。实验所采用的生物材料为骨髓细胞的细胞膜片,为较薄的组织,使用的脱细胞方法是化学去污剂(TritonX-100)联合物理洗涤的方法,避免了生物酶破坏细胞外基质的蛋白成分,最大程度上保证了细胞外基质蛋白成分含量和种类的完整性。非离子型洗涤剂TritonX-100可破坏蛋白与脂质、脂质与脂质、核酸和蛋白的链接,作用温和,可将细胞从较薄的组织上去除,而不破坏蛋白与蛋白之间的链接,因细胞外基质主要是各种蛋白成分交互连接而成的网状结构,有利于保护结构的完整性。实验扫描电镜显示,经脱细胞处理之后细胞外基质网状膜片完整无破损,无细胞残留,未见残存细胞核,说明此种去细胞方法可以有效去除细胞成分,获得细胞外基质膜片。
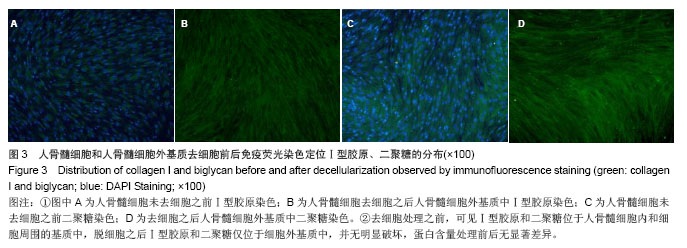
细胞外基质的主要成分为胶原蛋白、非胶原蛋白、蛋白多糖和弹性蛋白等,脱细胞处理之后相关蛋白保留与否成为评价脱细胞处理的指标之一。Dahms等
[14]对鼠、猪和人的膀胱脱细胞处理,并分析表明细胞外基质主要成分为Ⅰ型、Ⅲ型胶原和弹性蛋白。由此可见组织中的可溶性蛋白及细胞成分被去除,经过多步骤的脱细胞处理,保留下来的是具有完整外观形态和组织学及超微结构的不溶性基质成分, 主要是胶原、弹性蛋白、非胶原糖蛋白如层粘连蛋白、蛋白多糖和糖胺多糖等。实验中针对脱细胞处理前后进行Ⅰ型胶原、二聚糖免疫荧光染色显示,脱细胞处理前后细胞外的Ⅰ型胶原、二聚糖无明显不同,皆有序排列为网状结构。
细胞外基质作为基质微环境,调控着干细胞的自我更新和多向分化,在体外条件下能够减缓干细胞的老化
[15-16] 。那么细胞外基质到底是通过何种机制来影响干细胞的,引起了学术界极大的兴趣。大量研究表明,细胞外基质不仅可以通过组成成分来调节干细胞的多种生理活动,并且其物理机械性状可以影响干细胞的细胞形态和几何结构。众所周知,细胞外基质与干细胞的结合并非简单的物理黏附过程,而是细胞表面的跨膜异二聚体整合素介导了细胞外环境和细胞骨架的联系。整合素作为细胞外基质蛋白的主要受体,同时可以与表皮生长因子受体、血管内皮生长因子受体、血小板衍生生长因子受体、白细胞介素受体等生长因子、细胞因子受体相结合,进行双向信号传导
[17] 。整合素与相应受体结合后可产生一系列信号分子、组装多蛋白复合体、重组细胞骨架结构、激活Akt、Erk1/2等信号通路进而调节细胞黏附、迁移、增殖、生长和分化过程
[18] 。细胞外基质和整合素的相互作用能够调节细胞的黏附过程和激发信号传递已被广泛认同;并且越来越多的研究发现细胞外基质能够绑定某些重要的可溶性生长因子,将其固定在细胞外基质网状结构中
[19] 。已证实的细胞外基质蛋白,如纤连蛋白、玻连蛋白、胶原蛋白、蛋白多糖本身以及其与肝素和硫酸肝素的复合物可以绑定成纤维生长因子、肝细胞生长因子和血管内皮细胞等生长因子;Ⅱ、Ⅳ型胶原通过保守序列可以绑定骨形态蛋白2和转化生长因子β。因此,细胞外基质成为局部不溶性生长因子的储蓄库。基于此,生长因子锚定于细胞外基质之后可以通过两种途径来影响干细胞,一方面埋藏于细胞外基质蛋白中的生长因子可以作为锚定配体与干细胞表面的受体相结合,产生类似生长因子与对应受体结合所触发的信号传递;另一方面,细胞外基质蛋白或者蛋白多糖被蛋白酶降解之后释放被绑定的生长因子,游离的因子与受体结合也可引起一系列的细胞活动。所以,细胞外基质对干细胞的生物化学调节机制主要是通过细胞外基质与整合素、整合素与生长因子受体、细胞外基质与生长因子受体的相互作用所实现的。细胞外基质的物理机械硬度同样对于干细胞的分化起着至关重要的作用。Engler等
[20]发现类似于脑基质的合成材料促进干细胞分化为脑源性细胞,类似于骨骼肌基质的合成材料促进干细胞分化为肌细胞,而类似于骨基质的胶原材料则促使干细胞分化为成骨细胞。综上,可知细胞外基质是通过多种机制协调干细胞自我更新和多向分化的平衡。
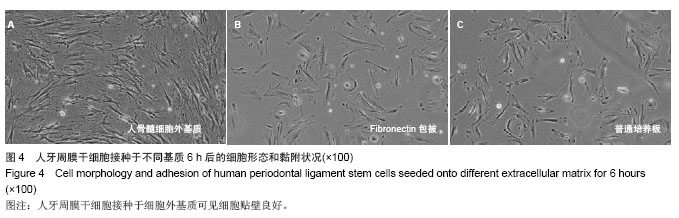
实验将人牙周膜干细胞细胞接种于人骨髓细胞外基质、Fibronectin包被的六孔板和普通培养板,6 h后观察细胞黏附情况发现,3组当中人骨髓细胞-细胞外基质组贴壁细胞数量最多,普通培养板贴壁细胞最少,说明细胞外基质可以加速细胞的贴壁速度;人骨髓细胞外基质组和纤粘连蛋白包被组比较可知,细胞与细胞外基质的结合不是简单的物理黏附,纤连蛋白因其物理性能可以黏附细胞,缩短细胞贴壁时间,但是图4可见人骨髓细胞外基质组人牙周膜干细胞失去原有形态,而是按照细胞外基质呈轨道样有序排列生长;相同天数观察细胞外基质组细胞明显多于其他两组,说明细胞外基质可以促进细胞的生长和增殖。与干细胞沿着细胞外基质的轨道生长,避免了接触抑制,从而促进干细胞的增殖的研究相一致。细胞外基质可以通过改变干细胞的形态来调控干细胞分化
[21] ,实验中在人骨髓细胞外基质上生长的人牙周膜干细胞细胞形态已经发生了一定的改变,作者猜测干细胞生长于组织特异性的细胞外基质可以改变干细胞的分化方向。
随着干细胞治疗在再生医学领域迅猛发展,对干细胞和细胞外基质之间相互关系的研究不断深入,细胞外基质的成功制备不仅可以作为一种生物材料应用于组织工程领域,而且对于深入研究细胞外基质对干细胞调控提供相关依据。
.jpg)